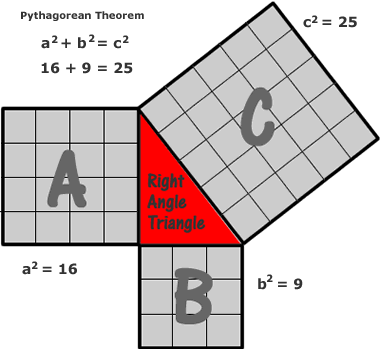
Pythagoras of Samos discovered a useful formula for finding the unknown side length of a right triangle.
He found that if you squared the length of the legs (base & height) of a right triangle; you can find the length of the hypotenuse by adding those two squares (a² + b²).
For example, lets say that the known legs (base & height) of the triangle are 3 & 4
3² + 4² = c²
Once you find the total of those two squared legs. You will find the square of the hypotenuse (the longest side of the triangle).
For example:
3² + 4² = 9 + 16 = 25 so c² = 25
Now that you have the square of the hypotenuse – find the square root of that number to acquire the actual length of that side.
√25 = 5
check out these links for a demonstration: